Abstract
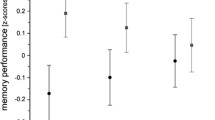
Cognitive functions show large variation in elderly people and are substantially heritable. Animal studies revealed that dynorphins influence cognition and memory, especially in aged animals. Thus, we tested the effect of four SNPs (rs7272891, rs1997794, rs2235751 and rs910080) and the VNTR promoter polymorphism in the prodynorphin gene (PDYN) on episodic memory and verbal fluency in a large (n = 1619) sample of elderly people (mean age: 80 ± 3.39 years; range 75–90 years) recruited through the German study on ageing, cognition and dementia in primary care patients (AgeCoDe). We found that carriers of the minor alleles of rs1997794 (P < 0.002) and rs910080 (P < 0.005) presented with higher episodic memory scores than homozygote carriers of the major allele. Also, a three marker haplotype including these two SNPs and rs2235751 was associated with better episodic memory scores. Verbal fluency scores were non-significantly better in carriers of these respective alleles. Thus, our results suggest a role of PDYN gene variations in determining memory function also in elderly humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardila A (2007) Normal aging increases cognitive heterogeneity: analysis of dispersion in WAIS-III scores across age. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 22:1003–1011
Becker T, Knapp M (2004) A powerful strategy to account for multiple testing in the context of haplotype analysis. Am J Hum Genet 75:561–570
Chandler MJ, Lacritz LH, Hynan LS, Barnard HD, Allen G, Deschner M, Weiner MF, Cullum CM (2005) A total score for the CERAD neuropsychological battery. Neurology 12:102–106
Collie A, Shafiq-Antonacci R, Maruff P, Tyler P, Currie J (1999) Norms and the effects of demographic variables on a neuropsychological battery for use in healthy ageing Australian populations. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 33:568–575
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39:175–191
Hauser KF, Aldrich JV, Anderson KJ, Bakalkin G, Christie MJ, Hall ED, Knapp PE, Scheff SW, Singh IN, Vissel B, Woods AS, Yakovleva T, Shippenberg TS (2005) Pathobiology of dynorphins in trauma and disease. Front Biosci 10:216–235
Hixson JE, Vernier DT (1990) Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 31:545–548
Itoh J, Ukai M, Kameyama T (1993) Dynorphin A-(1–13) potently prevents memory dysfunctions induced by transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 234:9–15
Jessen F, Wiese B, Cvetanovska G, Fuchs A, Kaduszkiewicz H, Kolsch H, Luck T, Mosch E, Pentzek M, Riedel-Heller SG, Werle J, Weyerer S, Zimmermann T, Maier W, Bickel H (2007) Patterns of subjective memory impairment in the elderly: association with memory performance. Psychol Med 37:1753–1762
Jiang HK, Owyang VV, Hong JS, Gallagher M (1989) Elevated dynorphin in the hippocampal formation of aged rats: relation to cognitive impairment on a spatial learning task. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2948–2951
Kotz CM, Weldon D, Billington CJ, Levine AS (2004) Age-related changes in brain proDynorphin gene expression in the rat. Neurobiol Aging 25:1343–1347
Kuzmin A, Madjid N, Terenius L, Ogren SO, Bakalkin G (2006) Big dynorphin, a prodynorphin-derived peptide produces NMDA receptor-mediated effects on memory, anxiolytic-like and locomotor behavior in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1928–1937
Luck T, Riedel-Heller SG, Kaduszkiewicz H, Bickel H, Jessen F, Pentzek M, Wiese B, Kölsch H, van den BH, Abholz HH, Moesch E, Gorfer S, Angermeyer MC, Maier W, Weyerer S (2007) Mild cognitive impairment in general practice: age-specific prevalence and correlate results from the German study on ageing, cognition and dementia in primary care patients (AgeCoDe). Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 24:307–316
McClearn GE, Johansson B, Berg S, Pedersen NL, Ahern F, Petrill SA, Plomin R (1997) Substantial genetic influence on cognitive abilities in twins 80 or more years old. Science 276:1560–1563
Meinzer M, Flaisch T, Wilser L, Eulitz K, Rockstroh B, Conway T, Gonzalez-Rothi L, Crosson B (2009) Neural signatures of semantic and phonemic fluency in young and old adults. J Cogn Neurosci [Epub ahead of print]
Miyajima F, Ollier W, Mayes A, Jackson A, Thacker N, Rabbitt P, Pendleton N, Horan M, Payton A (2008) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor polymorphism Val66Met influences cognitive abilities in the elderly. Genes Brain Behav 71:4–719
Nguyen XV, Masse J, Kumar A, Vijitruth R, Kulik C, Liu M, Choi DY, Foster TC, Usynin I, Bakalkin G, Bing G (2005) Prodynorphin knockout mice demonstrate diminished age-associated impairment in spatial water maze performance. Behav Brain Res 161:254–262
Nilsson LG, Adolfsson R, Backman L, Cruts M, Nyberg L, Small BJ, Van BC (2006) The influence of APOE status on episodic and semantic memory: data from a population-based study. Neuropsychology 20:645–657
Papassotiropoulos A, Stephan DA, Huentelman MJ, Hoerndli FJ, Craig DW, Pearson JV, Huynh KD, Brunner F, Corneveaux J, Osborne D, Wollmer MA, Aerni A, Coluccia D, Hanggi J, Mondadori CR, Buchmann A, Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Henke K, de Quervain DJ (2006) Common Kibra alleles are associated with human memory performance. Science 314:475–478
Ray R, Doyle GA, Crowley JJ, Buono RJ, Oslin DW, Patkar AA, Mannelli P, DeMaria PA Jr, O’Brien CP, Berrettini WH (2005) A functional prodynorphin promoter polymorphism and opioid dependence. Psychiatr Genet 15:295–298
Schaid DJ, Rowland CM, Tines DE, Jacobson RM, Poland GA (2002) Score tests for association between traits and haplotypes when linkage phase is ambiguous. Am J Hum Genet 70:425–434
Wagner M, Schuhmacher A, Schwab S, Zobel A, Maier W (2008) The His452Tyr variant of the gene encoding the 5-HT2A receptor is specifically associated with consolidation of episodic memory in humans. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:1163–1167
Weisskopf MG, Zalutsky RA, Nicoll RA (1993) The opioid peptide dynorphin mediates heterosynaptic depression of hippocampal mossy fibre synapses and modulates long-term potentiation. Nature 362:423–427
Welsh KA, Butters N, Mohs RC, Beekly D, Edland S, Fillenbaum G, Heyman A (1994) The consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part V. A normative study of the neuropsychological battery. Neurology 44:609–614
Xuei X, Dick D, Flury-Wetherill L, Tian HJ, Agrawal A, Bierut L, Goate A, Bucholz K, Schuckit M, Nurnberger J Jr, Tischfield J, Kuperman S, Porjesz B, Begleiter H, Foroud T, Edenberg HJ (2006) Association of the kappa-opioid system with alcohol dependence. Mol Psychiatry 11:1016–1024
Yakovleva T, Marinova Z, Kuzmin A, Seidah NG, Haroutunian V, Terenius L, Bakalkin G (2007) Dysregulation of dynorphins in Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Aging 28:1700–1708
Yuferov V, Ji F, Nielsen D A, Levran O, Ho A, Morgello S, Shi R, Ott J, Kreek MJ (2008) A functional haplotype implicated in vulnerability to develop cocaine dependence is associated with reduced PDYN expression in human brain. Neuropsychopharmacology doi:10.1038/npp.2008.187
Zimprich A, Kraus J, Woltje M, Mayer P, Rauch E, Hollt V (2000) An allelic variation in the human prodynorphin gene promoter alters stimulus-induced expression. J Neurochem 74:472–477
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the German Competence Network on Dementia (CND) and was funded by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (grants CNDD: 01 GI 0710 Hamburg, 01 GI 0711 Bonn, 01 GI 0712 Mannheim, 01 GI 0713 Düsseldorf, 01 GI 0714 Leipzig, 01 GI 0715 München, 01 GI 0716 Hannover, 01 GI 0717 Bremen). We thank Beisa Burnic, Christine Frahnert-Ledschbor, Sandra Schmitz and Anne Schulz for skillful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Kölsch and M. Wagner contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kölsch, H., Wagner, M., Bilkei-Gorzó, A. et al. Gene polymorphisms in prodynorphin (PDYN) are associated with episodic memory in the elderly. J Neural Transm 116, 897–903 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0238-5