Summary
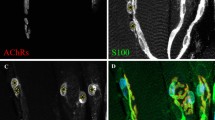
Terminal Schwann cells, when stained for S100 (a calcium binding protein), can be seen to cap motor axons at the neuromuscular junction. Within days of denervation the Schwann cells begin to stain for the low affinity nerve growth factor receptor, but remain Thy-1 negative, and elaborate fine processes. These processes become longer and more disorganized over weeks, and cells positive for S100 and nerve growth factor receptor migrate into the perisynaptic area. Reinnervation results in a withdrawal of the processes. The morphology and location of terminal Schwann cells seems to depend on axonal contact. The spread of Schwann cells and their processes away from the synaptic zone following denervation, implies that these cells do not target axons directly to the endplate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguayo, A. J., Epps, J., Charron, L. &Bray, G. M. (1976) Multipotentiality of Schwann cells in cross-anastomsis and graft in myelinated and unmyelinated nerves: quantitative microscopy and radioautography.Brain Research 104, 1–20.
Alderson, K., Pestronk, A., Woon-Che, Y. &Drachman, D. B. (1989) Silver cholinesterase immunocytochemistry: a new neuromuscular junction stain.Muscle & Nerve 12, 9–14.
Ard, M. D., Bunge, R. P. &Bunge, M. B. (1987) Comparison of the Schwann cell surface and Schwann cell extracellular matrix as promoters of neurite growth.Journal of Neurocytology 16, 539–57.
Baichwal, R. R., Bigbee, J. W. &De Vries, G. H. (1988) Macrophage-mediated myelin related mitogenic factor from cultured Schwann cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 85, 1701–5.
Bignami, A., Dahl, D., Nguyen, B. T. &Crosby, C. J. (1981) The fate of axonal debris in Wallerian degeneration of rat optic and sciatic nerves. Electron microscopy and immunofluorescence studies with neurofilament antisera.Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 40, 537–50.
Bignami, A., Chi, N. H. &Dahl, D. (1984) Laminin in rat sciatic nerve undergoing Wallerian degeneration.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurohgy 43, 94–103.
Billings-Gagliardi, S., Webster, H. De F. &O'Connell, M. F. (1974)In vivo and electronmicroscopic observation on Schwann cells in developing tadpole nerve fibres.American Journal of Anatomy 141, 375–92.
Bixby, J. L., Pratt, R. S., Lilien, J. &Reichardt, L. F. (1987) Neurite outgrowth on muscle cell surfaces involves extracellular matrix receptors as well as Ca2+-dependent and -independent cell adhesion molecules.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 2555–9.
Bixby, J. L., Lillien, J. &Reichardt, L. F. (1988) Identification of the major proteins that promote neuronal process outgrowth on Schwann cellsin vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 107, 353–61.
Brockes, J. P., Fields, K. L. &Raff, M. C. (1977) A surface antigenic marker for rat Schwann cells.Nature 266, 364–6.
Brockes, J. P., Fields, K. L. &Raff, M. C. (1979) Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. 1. Establishment of purified population for cultures of rat peripheral nerve.Brain Research 165, 105–18.
Brown, M. C., Holland, R. L. &Hopkins, W. G. (1981) Motor nerve sprouting.Annual Review of Neuroscience 4, 17–42.
Bunge, M. B., Williams, A. K. &Wood, P. M. (1982) Neuron-Schwann cell interaction in basai lamina formation.Developmental Biology 92, 449–60.
Caroni, P. &Grandes, P. (1990) Nerve sprouting in innervated adult skeletal muscle induced by exposure to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factors.Journal of Cell Biology 110, 1307–17.
Chandler, C. E., Parsons, L. M., Hosang, M. &Shooter, E. M. (1984) A monoclonal antibody modulates the interaction of nerve growth factor with PC 12 cells.Journal of Biological Chemistry 259, 6882–9.
Clark, M. B. &Bunge, M. B. (1989) Cultured Schwann cells assemble normal-appearing basal lamina only when they ensheath axons.Developmental Biology 133, 393–404.
Cocchia, D. &Michetti, F. (1981) S-100 antigen in satellite cells of the adrenal medulla and the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. An immunochemical and immuno-cytochemical study.Cell and Tissue Research 215, 103–112.
Connor, E. A. &Mcmahan, U. J. (1987) Cell accumulation in the junctional region of denervated muscle.Journal of Cell Biology 104, 109–20.
Covault, J. &Sanes, J. R. (1985) Neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) accumulates in denervated and paralysed skeletal muscle.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 82, 4544–8.
Covault, J., Cunningham, J. M. &Sanes, J. R. (1987) Neurite outgrowth on cryostat sections of innervated and denervated skeletal muscle.Journal of Cell Biology 105, 2479–88.
De Koning, P. &Gispen, W. H. (1987) Org.2766 improves functional and electrophysiological aspects of regenerating sciatic nerve in the rat.Peptides 8, 415–22.
Fadic, R., Brandan, E. &Inestrsa, N. C. (1990) Motor nerve regulates muscle extracellular matrix proteoglycan expression.Journal of Neuroscience 10, 3516–23.
Fallon, J. R. (1985) Preferential outgrowth of central nervous system neurites on astrocytes and Schwann cells as compared with non-glial cellsin vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 100, 198–207.
Fawcett, J. W. &Keynes, R. J. (1990) Peripheral nerve regeneration.Annual Review of Neuroscience 13, 43–60.
Gatchalian, C. L., Schachner, M. &Sanes, J. R. (1989) Fibroblasts that proliferate near denervated synaptic sites in skeletal muscle synthesize the adhesive molecules tenascin (J1), N-CAM, fibronectin, and a heparin sulfate proteoglycan.Journal of Cell Biology 108, 1873–90.
Gibson, S. J., Folak, J. M., Bloom, S. R., Sabate, I. M., Mulderry, P. M., Ghatei, M. A., Mcgregor, S. P., Morrison, J. F. B., Kelly, J. S., Evans, R. M. &Rosenfeld, M. G. (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and eight other species.Journal of Neuroscience 4, 3101–11.
Gorio, A., Carmignoto, G., Finesso, M., Polato, P. &Nunzi, M. G. (1983) Muscle reinnervation-II. Sprouting, synapse formation and repression.Neuroscience 8, 403–15.
Gutman, E. &Young, J. Z. (1944) The reinnervation of muscle after various periods of atrophy.Journal of Anatomy 78, 15–43.
Henderson, C. E., Huchet, M. &Changeux, J. P. (1983) Denervation increases a neurite-promoting activity in extracts of skeletal muscle.Nature 302, 609–11.
Heumann, R., Lindholm, D., Bandtlow, C., Meyer, M., Radeke, M. J., Misko, T. P., Shooter, E. &Thoenen, H. (1987a) Differential regulation of mRNA encoding nerve growth factor and its receptor in rat sciatic nerve during development degeneration and regeneration: Role of macrophages.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 8735–9.
Heumann, R., Korsching, S., Bandtlow, C. &Thoenen, H. (1987b) Changes in nerve growth factor synthesis in response to sciatic nerve transectionJournal of Cell Biology 104, 1623–31.
Hunter, D. D., Shah, U., Merlic, J. P. &Sanes, J. R. (1989) A lamin-like adhesive protein concentrated in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction.Nature 338, 229–34.
Ide, C., Tohyama, K., Yokota, R., Nitatori, T. &Onodera, S. (1983) Schwann cell basal lamina and nerve regeneration.Brain Research 288, 61–75.
Isobe, T., Takahashi, K. &Okuyama, T. (1984) S-100ao (alpha, alpha) protein is present in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system.Journal of Neurochemistry 43, 1494–6.
Jacobson, S. &Guth, L. (1965) An electrophysiological study of the early stages of peripheral nerve regeneration.Experimental Neurology 11, 48–56.
Jessen, K. R., Morgan, L., Brammer, M. &Mirsky, R. (1985) Galactocerebroside is expressed by non-myelin forming Schwann cellsin situ.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 1135–43.
Jessen, K. R., Mirsky, R. &Morgan, L. (1987) Myelinated but not unmyelinated axons, reversibly down-regulate N-CAM in Schwann cells.Journal of Neurocytology 16, 681–8.
Jessen, K. R., Morgan, L., Stewart, H. J. S. &Mirsky, R. (1990) Three markers of adult non-myelin forming Schwann cells, 217c(Ran-1), A5E3 and GFAP: development and regulation by neuron-Schwann cell interactions.Development 109, 91–103.
Keynes, R. J., Hopkins, W. G. &Brown, M. C. (1983) Sprouting of mammalian motorneurones at nodes of Ranvier: the role of the denervated motor endplate.Brain Research 264, 209–13.
Kligman, D. &Hilt, D. C. (1988) The S100 protein family.Trends in Biochemical Sciences 13, 437–443.
Kuffler, D. P. (1989) Regeneration of muscle axons in the frog is directed by diffusible factors from denervated muscle.Journal of Comparative Neurology 281, 416–25.
Lander, A. D., Fujii, D. K. &Reichardt, L. F. (1985) Laminin is associated with the ‘neurite outgrowthpromoting factors’ found in conditioned media.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 82, 2183–7.
Lubinska, L. (1977) Early course of Wallerin degeneration in myelinated fibres of the rat phrenic nerve.Brain Research 130, 47–63.
Manolov, S. (1974) Initial changes in the neuromuscular synapses of denervated rat diaphragm.Brain Research 65, 303–16.
Manthorpe, M., Engvall, E., Ruoslahti, E., Longo, F., Davis, G. &Varon, S. (1983) Lamina promotes neuritic regeneration from cultured peripheral and central neurons.Journal of Cell Biology 97, 1882–90.
Marshall, L. M., Sanes, J. R. &Mcmahan, U. J. (1977) Reinnervation of original synaptic sites on muscle fibre basement membrane after disruption of the muscle cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 74, 3073–77.
Mata, M., Alessi, D. &Fink, D. J. (1990) S100 is preferentially distributed in myelin-forming Schwann cells.Journal of Neurocytology 19, 432–42.
Matteoli, M., Haimann, C., Torri-Tarelli, F., Polak, J. M., Ceccarelli, B. &De Camilli, P. (1988) Differential effect of α-latrotoxin on exocytosis from small synaptic vesicles and from large dense core vesicles containing calcitonin gene-related peptide of the frog neuromuscular junction.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 85, 7366–70.
Mclean, I. W. &Nakane, P. K. (1974) Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixative for immunoelectron microscopy.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 22, 1077–83.
Mcmahan, U. J., Sanes, J. R. &Marshall, L. M. (1978) Cholinesterase is associated with the basal lamina at the neuromuscular junction.Nature 193, 281–2.
Mcquarrie, I. G., Grafstein, B. &Gershon, M. D. (1977) Axonal regeneration in the rat sciatic nerve: effects of a conditioning lesion and of dbcAMP.Brain Research 132, 443–52.
Miledi, R. &Slater, C. R. (1970) On the degeneration of rat neuromuscular junctions after nerve section.Journal of Physiology 207, 507–28.
Miller, F. D., Tetzlaff, W., Bisby, M. A., Fawcett, J. W. &Milner, R. J. (1989) Rapid induction of the major embryonic tubulin mRNA, T1 during nerve regeneration in rats.Journal of Neuroscience 9, 1452–63.
Mirsky, R., Winter, J., Abney, E. R., Pruss, R. M., Gavrilovic, J. &Raff, M. C. (1980) Myelin-specific proteins and glycolipids in rat Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes in culture.Journal of Cell Biology 84, 483–94.
Mora, M., Marchi, M., Polak, J. M., Gibson, S. J. &Cornelio, F. (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity at the human neuromuscular junction.Brain Research 492, 404–7.
Murray, M. A. &Robbins, N. (1982) Cell proliferation in denervated muscle: identity and origin of the dividing cells.Neuroscience 7, 1823–34.
Neuberger, T. J. &Cornbrooks, C. J. (1989) Transient modulation of Schwarm cell antigens after peripheral nerve transection and subsequent regeneration.Journal of Neurocytology 18, 695–710.
Payer, A. F. (1979) An ultrastructural study of Schwann cell response to axonal degeneration.Journal of Comparative Neurology 183, 365–84.
Ramon Y Cajal, S. (1928) (trans. 1959). Degeneration and regeneration of the nervous system (edited and translated byR. M. May) New York: Hafner Publishing Company.
Reiger, F., Frumet, M. &Edelman, G. M. (1985) N-CAM at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 285–93.
Rich, M. M. &Lichtman, J. W. (1989) In vivo visualization of pre- and postsynaptic changes during synapse elimination in reinnervated mouse muscle.Journal of Neuroscience 9, 1781–1805.
Sanes, J. R. (1989) Extracellular matrix molecules that influence neural development.Annual Review of Neuroscience 12, 521–46.
Sanes, J. R. &Covault, J. (1985) Axon guidance during reinnervation of skeletal muscle.Trends in Neuroscience 8, 523–8.
Sanes, J. R., Marshall, L. M. &Mcmahan, U. J. (1978) Reinnervation of muscle fibre basal lamina after removal of myofibres. Differentiation of regenerating axons at original synaptic sites.Journal of Cell Biology 78, 176–98.
Sanes, J. R., Schachner, M. &Covault, J. (1986) Expression of several adhesion macromolecules in embryonic, adult, and denervated adult skeletal muscle.Journal of Cell Biology 102, 420–31.
Seilheimer, B. &Schachner, M. (1988) Studies of adhesion molecules mediating interaction between cells of the peripheral nervous system indicate a major role for L1 in mediating sensory neuron growth on Schwann cells in culture.Journal of Cell Biology 107, 341–51.
Skene, H. J. P. (1989) Axonal growth-associated proteins.Annual Review of Neuroscience 12, 127–56.
Spreca, A., Rambotti, M. G., Rende, M., Saccardi, C., Aisa, M. L., Gianbanco, I. &Donato, R. (1989) Immunocytochemical localization of S-100b protein in degenerating and regenerating rat sciatic nerves.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 37, 441–6.
Stefansson, K., Wollmann, R. L. &Moore, B. W. (1982) Distribution of S-100 protein outside the central nervous system.Brain Research 234, 309–17.
Streit, W. J., Dumoulin, F. L., Raivich, &Kreutzberg, G. W. (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide increases in rat facial motoneurons after peripheral nerve transection.Neuroscience Letters 101, 143–8.
Stemple, D. L. &Anderson, D. J. (1991) A Schwann Cell antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody 217c is the low-affinity nerve growth receptor.Neuroscience Letters 124, 57–60.
Sugimura, K., Haimoto, H., Nagura, H., Kato, K. &Takahashi, A. (1989) Immunohistochemical differential distribution of S-100a and S100b in the peripheral nervous system of the rat.Muscle and Nerve 12, 929–35.
Sunderland, S. (1978)Nerves and Nerve Injuries. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Taniuchi, M., Clark, H. B. &Johnson, E. M. (1986) Induction of nerve growth factor receptor in Schwann cells after axotomy.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 83, 4094–8.
Taniuchi, M., Clark, H. B., Schweitzer, J. B. &Johnson, E. M. (1988) Expression of nerve growth factor receptors by Schwann cells of axotomized peripheral nerves: ultrastructural localization, suppression by axonal contact and binding properties.Journal of Neuroscience 8, 664–81.
Terenghi, G., Polak, J. M., Rodrigo, J., Mulderry, P. K. &Bloom, S. R. (1986) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerves in the tongue, epiglottis and pharynx of the rat: occurrence, distribution and origin.Brain Research 365, 1–14.
Traub, R. J., Iadarola, M. J. &Ruda, M. A. (1989) Effect of multiple dorsal rhizotomies on calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in the lumbosacral dorsal spinal cord of the cat: a radioimmunoassay analysis.Peptides 10, 979–83.
Wong, J. &Oblinger, M. M. (1990) A comparison of peripheral and central axotomy effects on neurofilament and tubulin gene expression in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons.Journal of Neuroscience 10, 2215–22.
Zuber, M. X., Goodman, D. W., Karns, L. R. &Fishman, M. C. (1989) The neuronal growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces filopodia in non-neuronal cells.Science 244, 1193–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds, M.L., Woolf, C.J. Terminal Schwann cells elaborate extensive processes following denervation of the motor endplate. J Neurocytol 21, 50–66 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206897
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206897